Bifidobacteria are living in the lower gastrointestinal tract of human and have various glycosidases that can degrade complex glycans. 1,3-1,4-α-L-Fucosidase from Bifidobacteria (AfcB) is involved in degradation of human milk oligosaccharides. AfcB specifically acts on Lewis a [Galβ1-3(Fucα1-4)GlcNAc-] and Lewis x [Galβ1-4(Fucα1-3)GlcNAc-] histo-blood group antigens.

QuickTime movie (2.1 MB) is here.
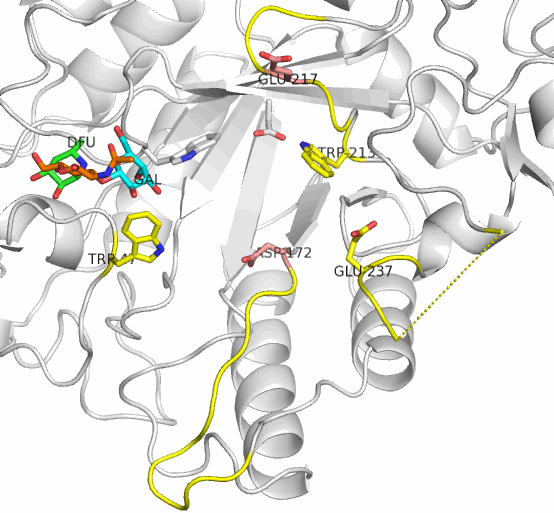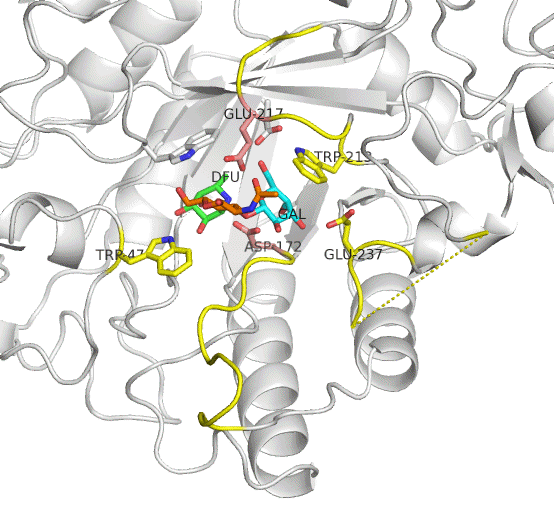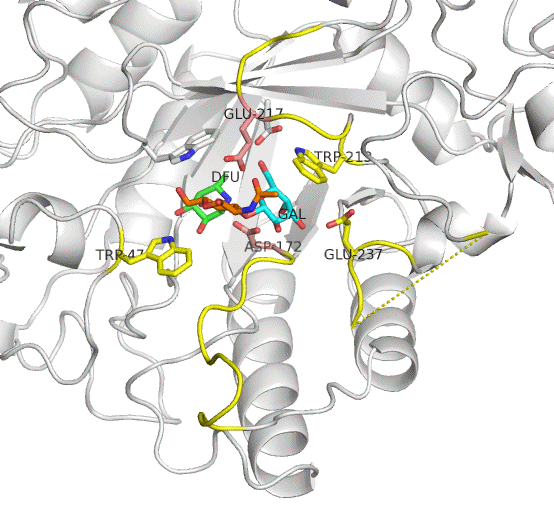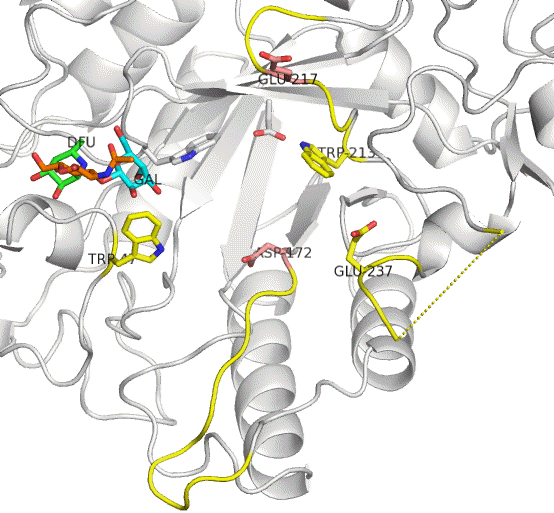
The active site residues of AfcB are Asp172 (nucleophile) and Glu217 (acid/base catalyst). Two loops carrying these residues largely move on substrate (Lewis a) binding to be placed at appropriate positions. This enzyme cleaves the fucose group (DFU, green). It is evident that AfcB strongly recognizes the galactose group (GAL, cyan) on substrate binding.
For details of this research, see our article on JBC.
H. Sakurama et al.
1,3-1,4-α-L-Fucosynthase that specifically introduces Lewis a/x antigens into type-1/2 chains
J. Biol. Chem. 287 (20), 16709-16719 (2012)
H. Sakurama, S. Fushinobu, and T. Katayama